DEUCALION
Supercomputer co-funded by FCT and EuroHPC, installed on the Azurém campus of the University of Minho. It is a national collaborative infrastructure to promote and support Open Science initiatives in supercomputing, data science and visualization. It seeks to be a sustainable computing and data infrastructure, aimed at national scientific and industrial communities, also articulating with international partners. Deucalion currently ranks 99th in energy efficiency of the Arm partition and 257th in processing speed in the TOP500 - November 2024 list.
This computing infrastructure is part of the RNCA - National Network for Advanced Computing - and offers High Performance Computing (HPC) resources with and without GPUs (Graphics processing unit) - for use by the research, technology and innovation/industry communities.
Contact: deucalion@support.macc.fccn.pt

A aquisição e a operação dos supercomputadores EuroHPC Deucalion e MareNostrum 5 são financiadas conjuntamente pela Iniciativa EuroHPC, através do Mecanismo Interligar a Europa da União Europeia e do programa de investigação e inovação Horizonte 2020, bem como pelos Estados participantes Portugal e Espanha para o Deucalion e Espanha, Portugal, Croácia e Turquia para o MareNostrum 5.
O Deucalion é gerido pela FCT, através da unidade de serviços digitais FCCN, com o apoio operacional do Centro Nacional de Computação Avançada (CNCA). A parte nacional é co-financiada pelo Investimento RE-C05-i08 “Ciência Mais Digital” do Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência – PRR.


More on funding for PROJECT DEUCALION
Operational from 2024
Specifications published on the EuroHPC website
One of the first 5 Petascale supercomputers co-financed by EuroHPC
Fujitsu PRIMEHPC A64FX (ARM partition) and Atos Bull Sequana AMD EPYC (x86 partition)
33 nodes with NVidia Ampere GPUs
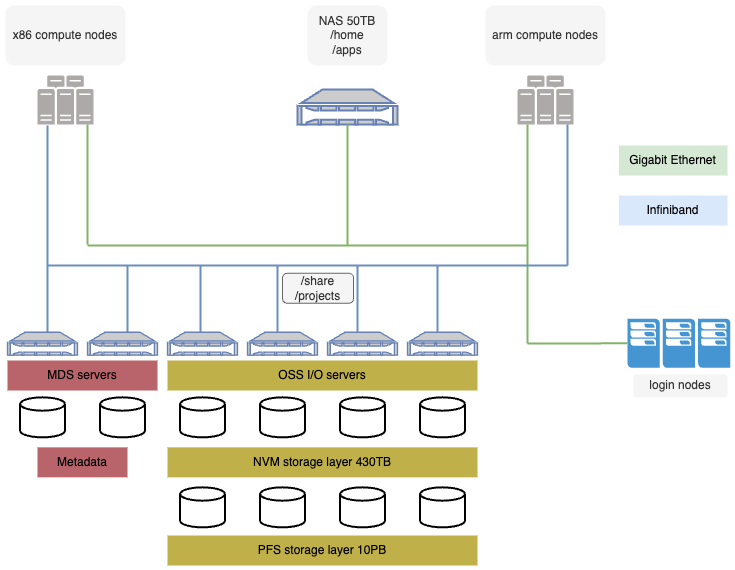
Storage with 430 TB High-speed NVMe partition and 10.6 PB high-speed based Parallel File System partition
10 PFlop maximum processing capacity
Partitions
Deucalion provides users with 3 partitions:


ARM
The ARM partition in Deucalion refers to the area of the supercomputer that uses processors based on the ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) architecture, known for its energy efficiency and performance.This ARM partition is therefore used to perform tasks that benefit from these characteristics, such as scientific simulations and large-scale data processing.
The ARM architecture is based on a reduced instruction set (RISC), which allows for a simpler and more efficient design, resulting in lower energy consumption and heat generation.
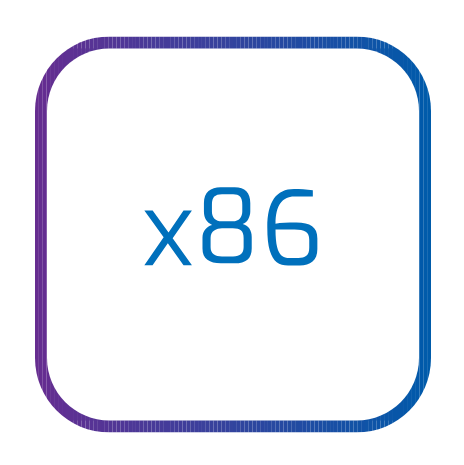
X86
The X86 partition in Deucalion uses processors based on the x86 architecture, originally developed by Intel and widely adopted in PCs, servers and supercomputers.
It is based on a complex instruction set (CISC), which offers a wide range of functionalities and support for a wide variety of software and applications.
The x86 partition is used to perform tasks that require high compatibility with existing software and that benefit from the robust performance offered by these processors. It is ideal for applications that require high processing power and need access to a vast ecosystem of development and optimization tools.
GPU
Deucalion's GPU partition is made up of 33 nodes based on x86 architecture, equipped with advanced Graphics Processing Units - GPUs - for optimizing parallel calculations and computationally intensive tasks.
Among these 33 nodes, 17 are equipped with NVIDIA A100 GPUs with 40GB of RAM, while the other 16 nodes have NVIDIA A100 GPUs with 80GB of RAM. A100 GPUs are known for their ability to deliver exceptional performance in artificial intelligence, machine learning and scientific computing applications, due to their highly parallel and efficient architecture.
Software
Using a combination of Linux operating systems optimized for HPC (high performance computing), Deucalion offers a robust and scalable environment for running intensive tasks.
Storage & Network
The storage system is designed to provide high capacity and speed, ensuring efficient and fast access to the large volumes of data required for scientific and industrial computing. Deucalion's network infrastructure uses cutting-edge technologies, such as InfiniBand, to offer low latency and high bandwidth.
Deucalion architecture
Access
Calls of Advanced Computing Projects
The RNCA organizes Calls for Advanced Computing Projects with the aim of allocating computing resources for research and innovation.
EuroHPC
Access to the EuroHPC portion of Deucalion is governed by the EuroHPC Joint Undertaking Access Policy. Information on access can be found on the dedicated EuroHPC Access page Calls .
Access Commercial
For computer projects that do not fall within the scope of the national Calls , it is possible to submit an access request, the associated costs of which will be calculated after the request has been analyzed.